Lesson 1-1 measuring segments and angles – Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of measurement with Lesson 1-1: Measuring Segments and Angles. This comprehensive guide unlocks the fundamental principles of segment and angle measurement, empowering you with the tools to navigate the world of geometry with precision and confidence.
Delve into the intricacies of line segments, unraveling their properties and the techniques for measuring them with precision. Discover the secrets of angle measurement, exploring the concepts of degrees and radians, and mastering the art of using a protractor. Prepare to classify angles into various categories, understanding their relationships and how to determine unknown angles.
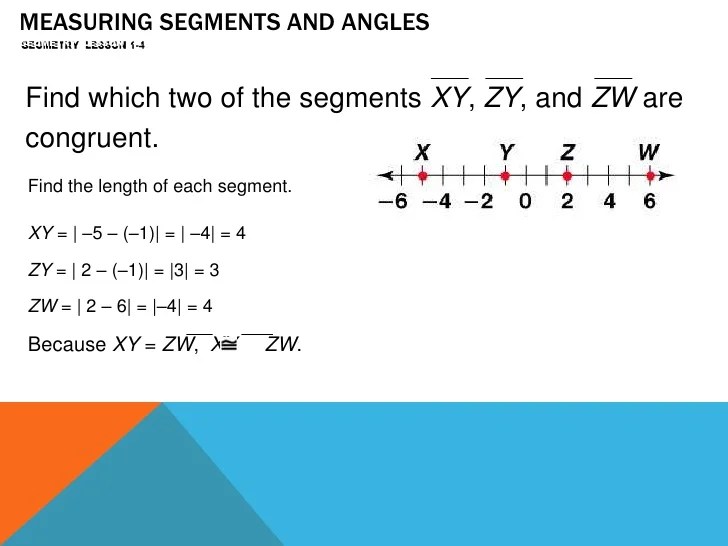
Segment Measurement: Lesson 1-1 Measuring Segments And Angles
Segment measurement involves determining the length of a line segment, which is a straight path between two points. To measure segments, we typically use a ruler or a protractor.
Units of measurement for segments include inches, centimeters, and meters. When using a ruler, it’s important to align the zero mark with one end of the segment and read the measurement at the other end.
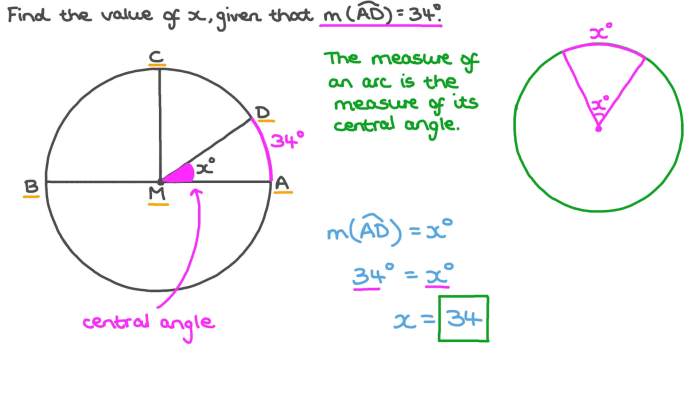
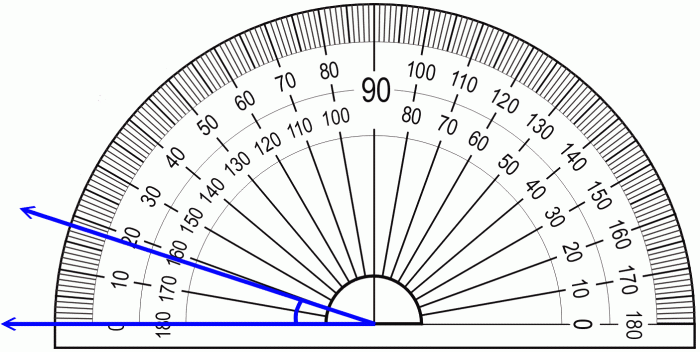
Angle Measurement
Angle measurement determines the size of an angle, which is formed by two rays that share a common endpoint called the vertex. To measure angles, we use a protractor.
Units of measurement for angles include degrees and radians. When using a protractor, we align the center mark with the vertex and read the measurement on the scale that corresponds to the angle’s rays.
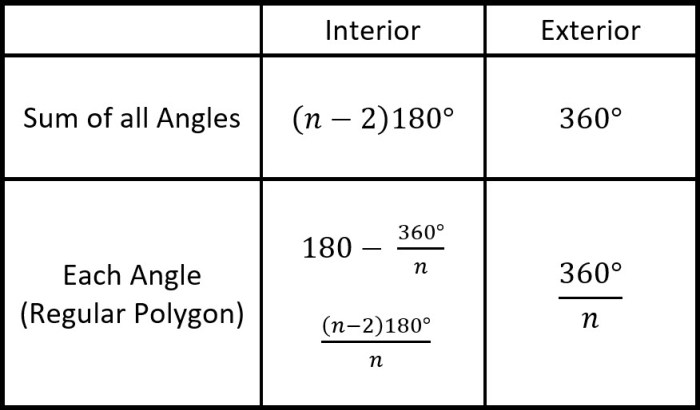
Types of Angles, Lesson 1-1 measuring segments and angles
Angles are classified into different types based on their measure:
- Acute angle: Less than 90 degrees
- Obtuse angle: Between 90 and 180 degrees
- Right angle: Exactly 90 degrees
- Straight angle: Exactly 180 degrees
Angle Relationships
Angles can have specific relationships with each other:
- Complementary angles: Add up to 90 degrees
- Supplementary angles: Add up to 180 degrees
- Vertical angles: Formed by two intersecting lines and opposite to each other
Applications of Segment and Angle Measurement
Segment and angle measurement have numerous real-world applications:
- Construction: Determining the lengths of beams and angles of roofs
- Navigation: Measuring distances and angles on maps
- Science: Measuring angles of incidence and reflection
Quick FAQs
What is the difference between a segment and an angle?
A segment is a part of a line, while an angle is formed by two rays that share a common endpoint.
How do I measure the length of a segment?
Use a ruler or measuring tape to determine the distance between the endpoints of the segment.
How do I measure the size of an angle?
Use a protractor to determine the number of degrees or radians between the two rays that form the angle.