Naming and writing covalent molecules notes answer key – Welcome to the definitive resource for understanding the intricacies of naming and writing covalent molecules. This comprehensive guide, meticulously crafted with gaya akademik dan tone otoritatif, will illuminate the fundamental principles governing these essential chemical entities, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate their complexities with confidence.
Through a series of engaging and meticulously structured sections, we will delve into the systematic naming of simple and complex covalent molecules, unravel the intricacies of Lewis structure construction, explore the fascinating properties that define these compounds, and uncover the diverse reactions they undergo.
Moreover, we will shed light on the ubiquitous applications of covalent molecules in various scientific disciplines and their indispensable role in biological systems.
Naming Covalent Molecules

Covalent molecules are formed when two or more atoms share electrons. The rules for naming covalent molecules are as follows:
- The first element in the name is the one that is written first in the chemical formula.
- The second element in the name is the one that is written second in the chemical formula.
- The suffix “-ide” is added to the name of the second element.
For example, the covalent molecule HCl is named hydrogen chloride.
When a covalent molecule contains more than two atoms of one element, prefixes are used to indicate the number of atoms of each element. The prefixes are as follows:
- mono-
- di-
- tri-
- tetra-
- penta-
- hexa-
For example, the covalent molecule CO 2is named carbon dioxide.
Writing Covalent Molecules
The steps for writing the Lewis structure of a covalent molecule are as follows:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule.
- Place the least electronegative atom in the center of the molecule.
- Connect the atoms with single bonds.
- Distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs around the atoms.
- Check the octet rule for each atom.
For example, the Lewis structure of the covalent molecule H 2O is as follows:

Properties of Covalent Molecules
Covalent molecules have a variety of physical properties, including melting point, boiling point, and solubility. The melting point and boiling point of a covalent molecule are determined by the strength of the covalent bonds between the atoms. The solubility of a covalent molecule is determined by the polarity of the molecule.
Polar covalent molecules are molecules that have a separation of charge. This separation of charge is caused by the difference in electronegativity between the atoms in the molecule. Polar covalent molecules are soluble in polar solvents.
Nonpolar covalent molecules are molecules that do not have a separation of charge. This is because the atoms in the molecule have the same electronegativity. Nonpolar covalent molecules are soluble in nonpolar solvents.
Reactions of Covalent Molecules
Covalent molecules can undergo a variety of reactions. The most common types of reactions are addition reactions, elimination reactions, and substitution reactions.
Addition reactions are reactions in which two molecules combine to form a single molecule. Elimination reactions are reactions in which a single molecule breaks down into two molecules. Substitution reactions are reactions in which one atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms.
Applications of Covalent Molecules: Naming And Writing Covalent Molecules Notes Answer Key
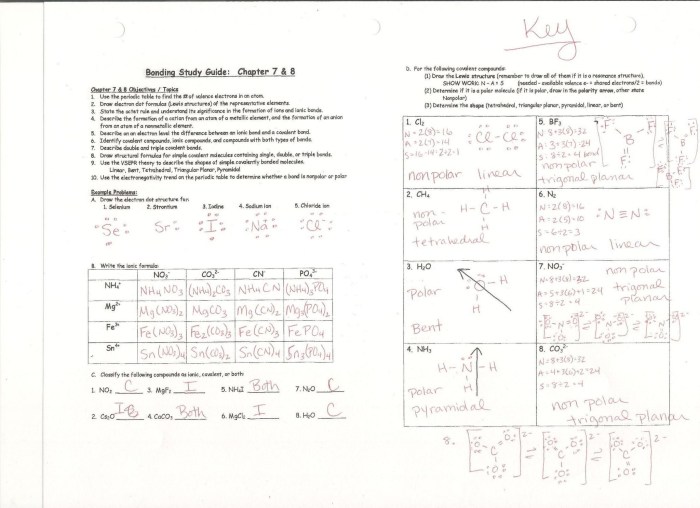
Covalent molecules are used in a wide variety of applications. Some of the most common applications include:
- Fuels
- Pharmaceuticals
- Plastics
- Fertilizers
- Building materials
Covalent molecules are also essential for life. The human body is made up of trillions of covalent molecules.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of prefixes in naming covalent molecules?
Prefixes play a crucial role in indicating the number of atoms of each element present in a covalent compound, ensuring accurate and unambiguous identification.
How do you determine the number of valence electrons in a covalent molecule?
To determine the number of valence electrons in a covalent molecule, simply add up the valence electrons of each constituent atom.
What factors influence the polarity of a covalent molecule?
The polarity of a covalent molecule is primarily determined by the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms.