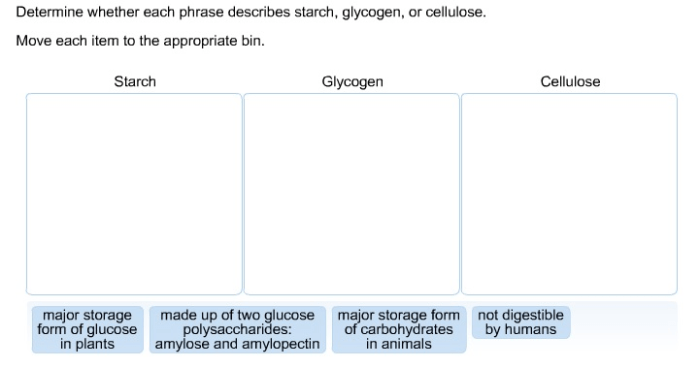
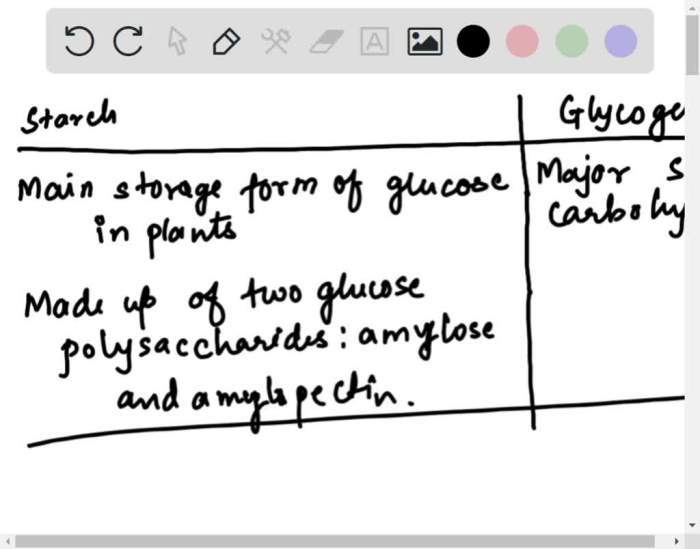
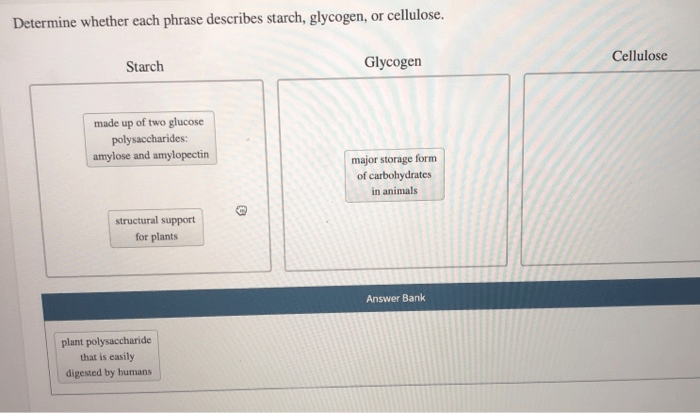
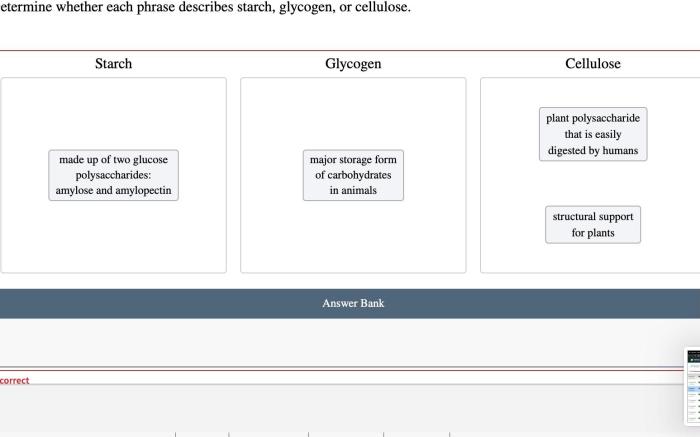
Determine whether each phrase describes starch glycogen or cellulose – In the realm of biochemistry, discerning the distinct characteristics of starch, glycogen, and cellulose is paramount. These polysaccharides exhibit unique structural and functional properties that shape their roles in biological systems and industrial applications. This discourse delves into the intricacies of each molecule, exploring their chemical composition, functional properties, and biological significance.
The structural comparison of these polysaccharides reveals variations in their molecular composition and arrangement. Starch, a complex carbohydrate found in plants, comprises amylose and amylopectin, while glycogen, the primary energy reserve in animals, consists of highly branched glucose units. Cellulose, on the other hand, is a linear polymer of glucose molecules found in plant cell walls, providing structural support.
Structural Comparison
Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all polysaccharides, but they differ in their chemical structure and arrangement.
Starch and glycogen are both branched polymers of glucose, but starch is a more complex molecule with a larger molecular weight. Cellulose, on the other hand, is a linear polymer of glucose.
The following table compares the chemical structure of starch, glycogen, and cellulose:
| Polysaccharide | Chemical Structure | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Starch | Branched polymer of glucose | 100,000
|
| Glycogen | Branched polymer of glucose | 200,000
|
| Cellulose | Linear polymer of glucose | 500,000
|
Functional Properties
The different structures of starch, glycogen, and cellulose give them different functional properties.
Starch is a storage form of glucose that is used by plants as a source of energy. Glycogen is also a storage form of glucose, but it is used by animals as a source of energy.
Cellulose is a structural component of plant cell walls. It provides strength and rigidity to the cell wall.
Biochemical Pathways
The synthesis and degradation of starch, glycogen, and cellulose are complex biochemical pathways.
The synthesis of starch is catalyzed by the enzyme starch synthase. The synthesis of glycogen is catalyzed by the enzyme glycogen synthase. The synthesis of cellulose is catalyzed by the enzyme cellulose synthase.
The degradation of starch is catalyzed by the enzyme starch phosphorylase. The degradation of glycogen is catalyzed by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase. The degradation of cellulose is catalyzed by the enzyme cellulase.
Biological Significance
Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all important biological molecules.
Starch is a major source of energy for plants. Glycogen is a major source of energy for animals. Cellulose is a major structural component of plant cell walls.
Industrial Applications: Determine Whether Each Phrase Describes Starch Glycogen Or Cellulose
Starch, glycogen, and cellulose have a wide range of industrial applications.
Starch is used in the food industry as a thickener and binder. Glycogen is used in the pharmaceutical industry as a drug delivery system. Cellulose is used in the paper industry as a source of paper pulp.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary structural difference between starch and glycogen?
Starch consists of amylose and amylopectin, while glycogen is highly branched, resulting in a more compact structure.
How does the structure of cellulose contribute to its function?
Cellulose’s linear structure and strong hydrogen bonding provide rigidity and tensile strength, making it an essential component of plant cell walls.