After the wall around Jerusalem was rebuilt, the city embarked on a new chapter, marked by profound transformations that shaped its destiny. This pivotal event not only enhanced Jerusalem’s security but also ignited a cascade of social, economic, and religious changes, leaving an enduring legacy that continues to resonate today.
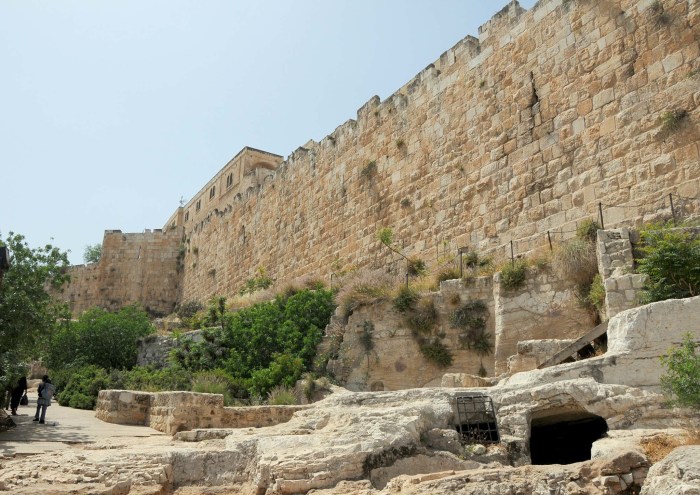
The rebuilding process, fraught with challenges and obstacles, tested the resilience of Jerusalem’s inhabitants. Yet, through their unwavering determination and innovative techniques, the wall was meticulously reconstructed, providing a formidable barrier against potential threats.
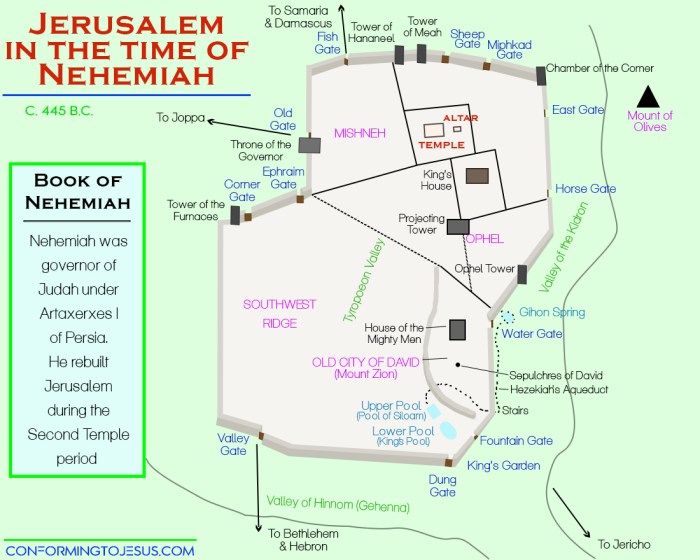
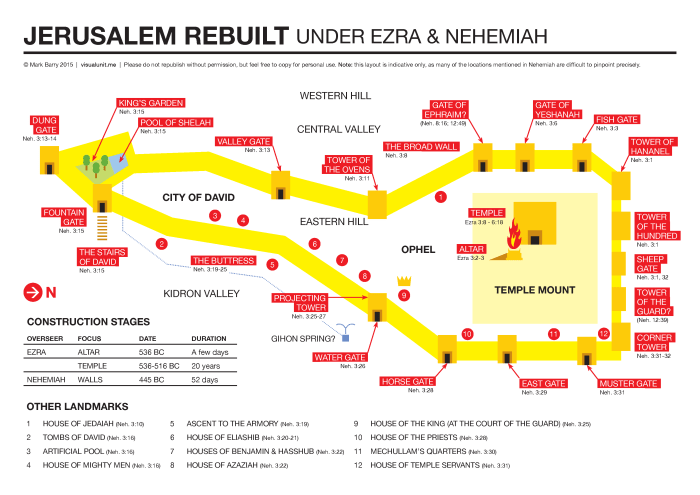
Historical Context: After The Wall Around Jerusalem Was Rebuilt

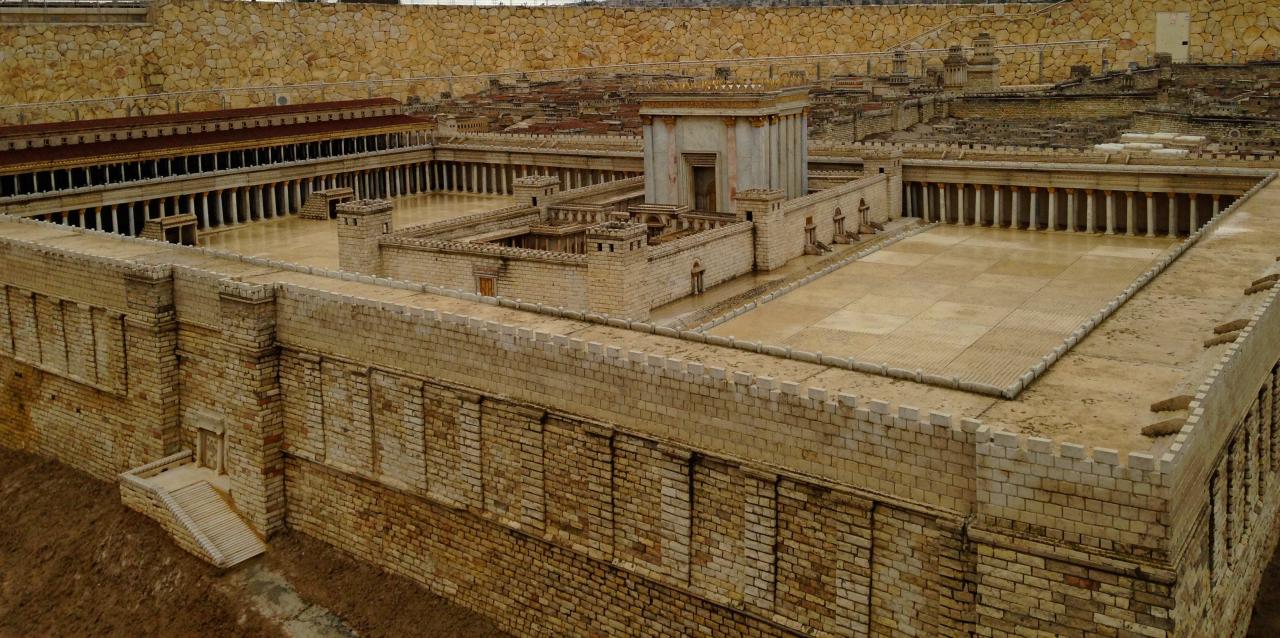
Jerusalem has a long and storied history, dating back to the Bronze Age. The city was a major religious and cultural center for the Jewish people, and it was also the capital of the Kingdom of Israel. In 586 BC, Jerusalem was destroyed by the Babylonians, and the city’s walls were torn down.
The rebuilding of the wall around Jerusalem was a major undertaking that took place in the 5th century BC. The project was led by the Persian king Artaxerxes I, and it was completed in 445 BC. The new wall was much larger and stronger than the old one, and it helped to protect the city from attack.
The Rebuilding Process
The rebuilding of the wall around Jerusalem was a massive undertaking that took place over several years. The project was supervised by the governor of Judah, Nehemiah, and it involved the cooperation of thousands of workers.
The wall was built using a variety of materials, including stone, wood, and earth. The stones were quarried from the nearby hills, and the wood was brought from Lebanon. The earth was used to fill in the gaps between the stones.
The wall was built in sections, and each section was completed by a different group of workers. The workers used a variety of tools and techniques to build the wall, including hammers, chisels, and levers.
Impact on Jerusalem
The rebuilding of the wall around Jerusalem had a major impact on the city. The new wall made the city more secure, and it also helped to boost the city’s economy. The wall also had a significant religious impact, as it made it easier for the Jewish people to worship at the Temple in Jerusalem.
The rebuilding of the wall also had a number of social and economic consequences. The new wall made it easier for the city to defend itself, but it also made it more difficult for people to enter and leave the city.
The wall also led to a rise in the cost of living in Jerusalem, as the city became more popular and more desirable to live in.
Religious and Cultural Significance
The wall around Jerusalem has great religious and cultural significance for the Jewish people. The wall is mentioned in the Bible, and it is considered to be a symbol of the Jewish people’s covenant with God.
The wall is also a major tourist attraction, and it is visited by millions of people each year. The wall is a reminder of the long and storied history of Jerusalem, and it is a symbol of the city’s resilience and strength.
Symbolism and Legacy, After the wall around jerusalem was rebuilt
The wall around Jerusalem has been used as a symbol of resilience and strength for centuries. The wall has been rebuilt many times over the centuries, and it has always stood as a symbol of the Jewish people’s determination to survive and thrive.
The wall is also a symbol of the city of Jerusalem itself. The wall has helped to protect the city from attack, and it has also helped to define the city’s identity. The wall is a reminder of the city’s long and storied history, and it is a symbol of the city’s resilience and strength.
Essential Questionnaire
Why was the wall around Jerusalem rebuilt?
The wall was rebuilt to strengthen Jerusalem’s defenses and protect it from potential invasions.
What were the challenges faced during the rebuilding process?
The challenges included sourcing materials, overcoming opposition from neighboring kingdoms, and managing the logistics of a large-scale construction project.
How did the rebuilt wall impact Jerusalem’s economy?
The wall stimulated economic growth by facilitating trade and commerce, as merchants felt more secure transporting goods within the city.