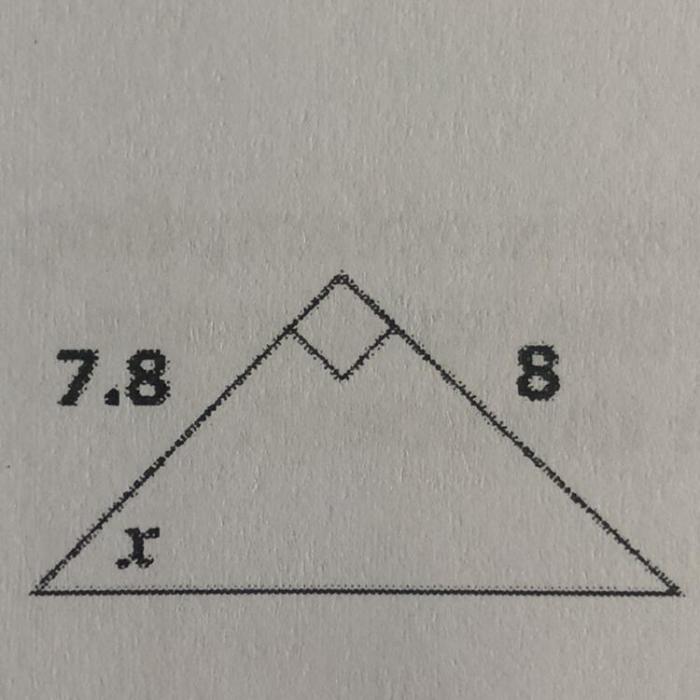
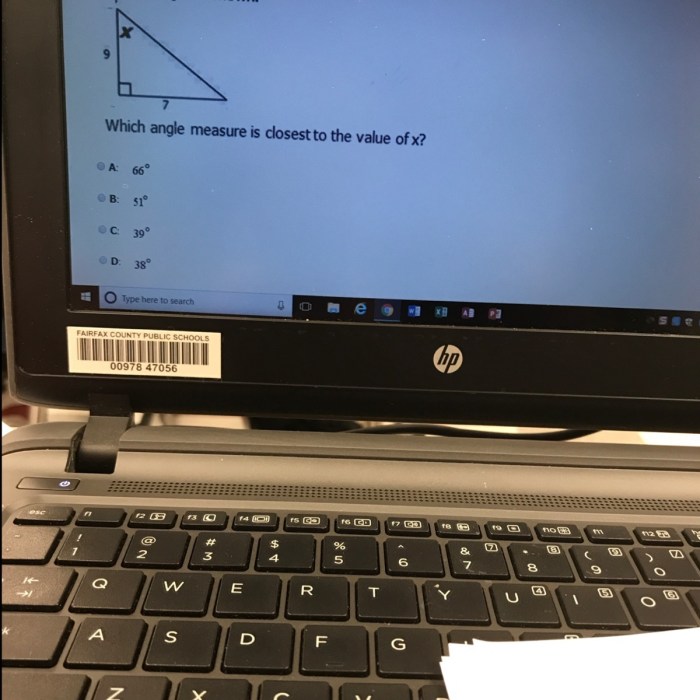
Which angle measure is closest to the value of x? This question delves into the realm of angle measurement, a fundamental concept in geometry with far-reaching applications. From architecture to engineering and navigation, precise angle measurement is paramount, and this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
In this exploration, we will delve into the concept of angle measure, its units, and various types of angles. We will discuss methods for measuring angles using protractors and other tools, exploring their accuracy and limitations. The importance of approximating and estimating angle measures will be highlighted, along with strategies for doing so based on visual cues and mental calculations.
Angle Measure Concepts
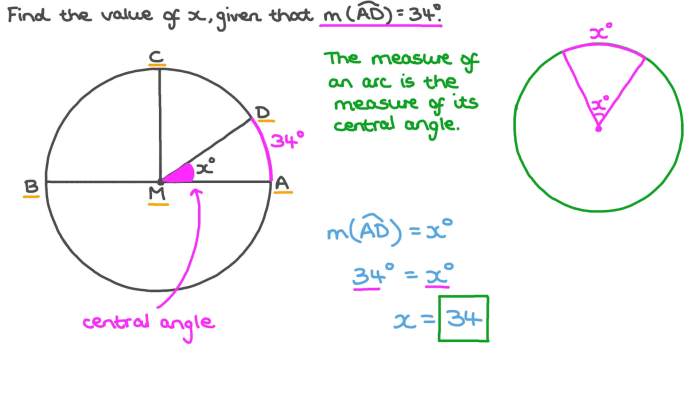
Angle measure is the quantification of the amount of rotation between two rays or line segments sharing a common endpoint, known as the vertex. The standard unit of angle measure is the degree (°), which represents 1/360th of a full rotation.
Another unit of angle measure is the radian (rad), which represents the angle formed by an arc length equal to the radius of a circle.
Types of Angles
- Acute angle:An angle less than 90° (π/2 radians).
- Right angle:An angle exactly equal to 90° (π/2 radians).
- Obtuse angle:An angle greater than 90° but less than 180° (π radians).
- Straight angle:An angle exactly equal to 180° (π radians).
- Reflex angle:An angle greater than 180° but less than 360° (2π radians).
Measurement Techniques: Which Angle Measure Is Closest To The Value Of X
Protractors, Which angle measure is closest to the value of x
Protractors are semi-circular tools with degree markings used to measure angles. To use a protractor, place its center point at the vertex of the angle and align its baseline with one of the rays. Read the angle measure where the other ray intersects the protractor’s scale.
Transportir
Transportir adalah alat ukur sudut yang berbentuk setengah lingkaran dengan skala derajat yang tertera di tepinya. Cara menggunakan transportir adalah dengan meletakkan titik pusat transportir pada titik sudut dan mencocokkan salah satu sisinya dengan salah satu kaki sudut. Besar sudut dapat dibaca pada skala derajat di mana kaki sudut lainnya memotong transportir.
Other Tools
Other tools for measuring angles include транспортиры, clinometers, and goniometers, each designed for specific applications and precision requirements.
Accuracy and Limitations
The accuracy of angle measurement depends on the tool used and the skill of the user. Protractors and транспортиры typically provide a precision of ±0.5°, while more specialized tools can achieve higher accuracy.
Approximation and Estimation
When precise angle measurement is not possible, approximation and estimation techniques become important. Visual cues, such as comparing angles to familiar shapes (e.g., a right angle to a corner of a book), can provide rough estimates.
Mental calculations can also be used to estimate angles. For example, an angle that appears to be slightly less than 90° can be estimated as approximately 80° or 85°.
Angle Classification
Angles are classified based on their measure:
| Angle Type | Measure Range |
|---|---|
| Acute angle | 0° to 90° |
| Right angle | Exactly 90° |
| Obtuse angle | 90° to 180° |
| Straight angle | Exactly 180° |
| Reflex angle | 180° to 360° |
Angle Relationships
Angles that share a common vertex or side have specific relationships:
Adjacent Angles
Adjacent angles are angles that share a common vertex and side. The sum of the measures of adjacent angles is equal to 180°.
Supplementary Angles
Supplementary angles are angles that have a sum of 180°. They can be adjacent or non-adjacent.
Complementary Angles
Complementary angles are angles that have a sum of 90°. They can be adjacent or non-adjacent.
Real-World Applications
Angle measure finds applications in various fields:
- Architecture:Designing buildings, determining roof angles, and calculating the angle of incidence of sunlight.
- Engineering:Measuring angles of joints, calculating the forces acting on structures, and designing bridges.
- Navigation:Determining the angle between a ship’s course and a destination, and calculating the angle of elevation of a celestial body.
Accurate angle measurement is crucial in these applications to ensure structural integrity, efficient operation, and precise navigation.
Questions Often Asked
What is the difference between an acute and an obtuse angle?
An acute angle is less than 90 degrees, while an obtuse angle is greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
How can I measure an angle without a protractor?
You can use a compass and ruler to construct a protractor or estimate the angle based on visual cues and mental calculations.
Why is accurate angle measurement important in real-world applications?
Accurate angle measurement is crucial in fields such as architecture, engineering, and navigation, where even small errors can have significant consequences.