Match the division of the vertebral column with its description. – The vertebral column, or backbone, is a complex structure composed of 33 individual bones called vertebrae. Each vertebra is categorized into one of five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, and coccyx. These regions vary in size, shape, and function, contributing to the overall flexibility and support of the spine.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the unique characteristics and functions of each vertebral region, providing a detailed understanding of their contributions to the overall structure and mechanics of the human body.
Match the Division of the Vertebral Column with Its Description
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is a complex structure that forms the central axis of the skeletal system. It consists of a series of bones called vertebrae, which are stacked one on top of another to form a flexible yet supportive framework.
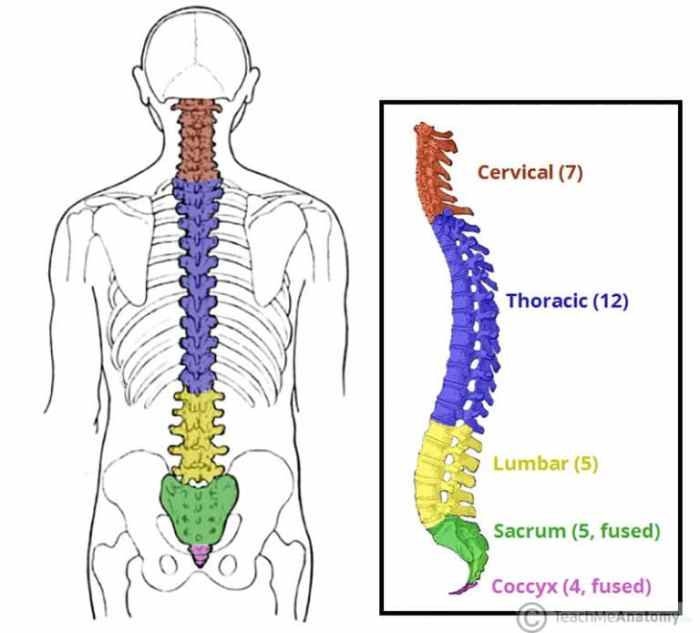
Each vertebral region exhibits unique characteristics and functions that contribute to the overall stability and mobility of the body.The vertebral column can be divided into five main regions: cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, and coccyx. Each region has its own distinct features, functions, and articulations, which will be explored in detail in the following sections.
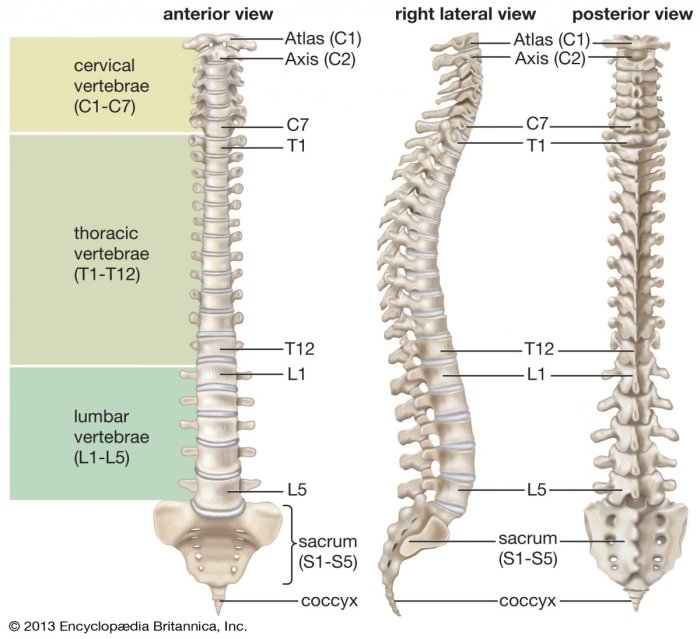
1. Cervical Vertebrae, Match the division of the vertebral column with its description.
The cervical vertebrae are the seven vertebrae located in the neck region. They are the smallest and most delicate of all the vertebrae and are highly mobile, allowing for a wide range of head and neck movements. The first cervical vertebra, known as the atlas, is unique in that it does not have a body and instead consists of two lateral masses that articulate with the occipital condyles of the skull.
The second cervical vertebra, called the axis, has a prominent odontoid process that projects upwards and articulates with the atlas, allowing for rotational movements of the head.The cervical vertebrae are responsible for supporting the weight of the head and facilitating a wide range of movements, including flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation.
They also provide protection for the delicate structures of the spinal cord and nerve roots that pass through the vertebral canal.
2. Thoracic Vertebrae
The thoracic vertebrae are the twelve vertebrae located in the chest region. They are larger and stronger than the cervical vertebrae and have a more complex structure. Each thoracic vertebra has a body that articulates with the ribs via costal facets, forming the rib cage.
The rib cage protects the vital organs of the thorax, including the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels.The thoracic vertebrae are relatively immobile compared to the cervical vertebrae, but they still allow for some flexion, extension, and lateral flexion. They also provide attachment points for muscles that assist in respiration and other movements of the trunk.
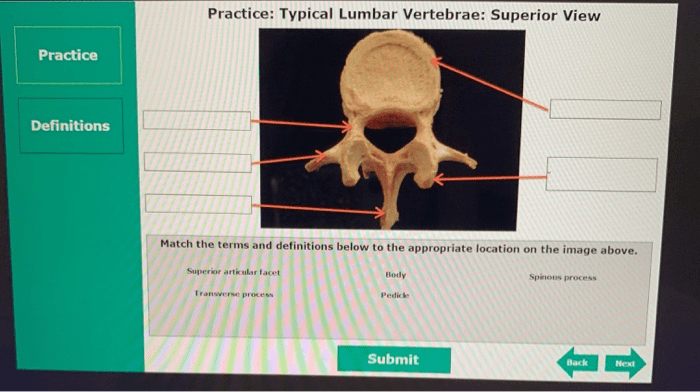
3. Lumbar Vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are the five vertebrae located in the lower back region. They are the largest and strongest of all the vertebrae and are designed to support the weight of the upper body and facilitate a wide range of movements.
The lumbar vertebrae have large, kidney-shaped bodies and robust processes that provide attachment points for muscles and ligaments.The lumbar vertebrae are responsible for supporting the weight of the body, transmitting forces from the upper body to the pelvis, and facilitating a variety of movements, including flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation.
They also provide protection for the spinal cord and nerve roots that pass through the vertebral canal.
4. Sacrum and Coccyx
The sacrum is a triangular bone formed by the fusion of five sacral vertebrae. It is located at the base of the spine and articulates with the ilium of the pelvis on each side. The sacrum provides support for the pelvic organs and transmits forces from the upper body to the pelvis.
It also provides attachment points for muscles and ligaments that stabilize the pelvis and spine.The coccyx is a small, triangular bone located at the very end of the spine. It is formed by the fusion of four coccygeal vertebrae and is vestigial in humans.
The coccyx provides some support for the pelvic floor muscles and helps to stabilize the pelvis.
5. Vertebral Column as a Whole
The vertebral column as a whole forms a flexible yet supportive framework that protects the spinal cord and nerve roots, supports the weight of the body, and facilitates a wide range of movements. Each vertebral region has its own unique characteristics and functions, contributing to the overall stability and mobility of the spine.The
following table summarizes the key features and functions of each vertebral region:| Region | Size and Shape | Articulations | Functions ||—|—|—|—|| Cervical Vertebrae | Small and delicate | Atlas and axis with skull, other cervical vertebrae | Support head, facilitate head and neck movements || Thoracic Vertebrae | Larger and stronger | Ribs, other thoracic vertebrae | Protect vital organs, facilitate respiration || Lumbar Vertebrae | Largest and strongest | Sacrum, other lumbar vertebrae | Support body weight, facilitate trunk movements || Sacrum | Triangular, fused | Ilium of pelvis | Support pelvic organs, transmit forces || Coccyx | Small, triangular, fused | None | Support pelvic floor muscles, stabilize pelvis |The vertebral column is a complex and highly adaptable structure that plays a vital role in supporting the body, protecting delicate structures, and facilitating a wide range of movements.
Understanding the unique characteristics and functions of each vertebral region is essential for comprehending the overall function of the spine and the musculoskeletal system as a whole.
Quick FAQs: Match The Division Of The Vertebral Column With Its Description.
What is the function of the cervical vertebrae?
The cervical vertebrae provide support for the head and allow for a wide range of neck movements, including flexion, extension, rotation, and lateral flexion.
How do the thoracic vertebrae differ from the lumbar vertebrae?
Thoracic vertebrae are larger and have longer spinous processes than lumbar vertebrae. They also have facets that articulate with the ribs, forming the rib cage and protecting vital organs.
What is the role of the sacrum and coccyx?
The sacrum and coccyx are fused structures that provide stability and support for the pelvic organs. They also serve as attachment points for muscles and ligaments.